Choosing the right commercial battery storage is crucial for businesses aiming for efficiency and sustainability. According to Margaret Lee, a recognized expert in the Commercial Battery Storage industry, “The right battery system can transform your energy management strategy.” This statement emphasizes the importance of making informed choices.
In today's market, the options can be overwhelming. From lithium-ion to flow batteries, each type has distinct advantages. Selecting the wrong system can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs. Companies must consider their specific energy needs carefully. Size, capacity, and discharge rates play vital roles in decision-making.
Additionally, many businesses overlook the integration of these systems with existing infrastructure. Compatibility can be a challenge, and improper pairing might result in waste. Reflecting on these factors is essential for achieving the desired energy goals. Entering the realm of Commercial Battery Storage requires thoughtful consideration and strategic planning.

When selecting the right commercial battery storage system, it’s crucial to understand the various technologies available. Lithium-ion batteries are prevalent in the market. They offer high energy density and efficient performance. According to a recent report, they account for over 70% of the commercial battery storage market. This popularity reflects their reliability and longevity, making them a common choice for many businesses.
However, there are other options worth considering. Lead-acid batteries are often cheaper and easier to recycle. They may not last as long as lithium-ion, but their lower upfront costs can benefit smaller businesses. Flow batteries are another alternative. They allow for longer discharge times and might support larger energy needs. A report shows that flow batteries could grow at an annual rate of 14% by 2026. This highlights their potential for future applications.
While these technologies have advantages, each comes with drawbacks. Lithium-ion systems can be expensive. Additionally, the sourcing of materials raises ethical concerns. Lead-acid batteries, while affordable, require frequent maintenance and have shorter lifespans. Companies must weigh these factors carefully. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each option is essential for making informed decisions.
| Battery Type | Energy Capacity (kWh) | Power Rating (kW) | Cycle Life (Number of Cycles) | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | 100 - 5000 | 5 - 3000 | 2000 - 5000 | Peak shaving, backup power |
| Lead-acid | 50 - 3000 | 1 - 200 | 500 - 1000 | Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) |
| Flow Batteries | 100 - 10000 | 10 - 200 | 3000 - 10000 | Renewable integration, long duration storage |
| Nickel Cadmium | 50 - 1500 | 5 - 50 | 1500 - 2000 | Telecom, remote applications |
Understanding your business's energy needs is crucial. Many companies underestimate their consumption. A report by the U.S. Energy Information Administration indicates that small businesses can use 30% more energy than assumed. Monitoring usage patterns over time can reveal significant insights. For instance, peak demand periods often lead to higher electricity bills.
Analyzing energy data helps identify opportunities for savings. Implementing energy management systems can enhance awareness. A study by the International Energy Agency shows that businesses that actively measure and analyze their energy usage can reduce costs by 10-20%. It’s eye-opening to realize how much waste can occur during non-peak hours.
Consider your operational hours and the nature of your equipment. Demand spikes can dramatically influence energy costs. Not all appliances draw power consistently. Factor in inefficiencies. Many businesses miss out by not benchmarking their usage against industry standards. Real data can prompt necessary adjustments. Your energy strategy should adapt to changing consumption patterns.
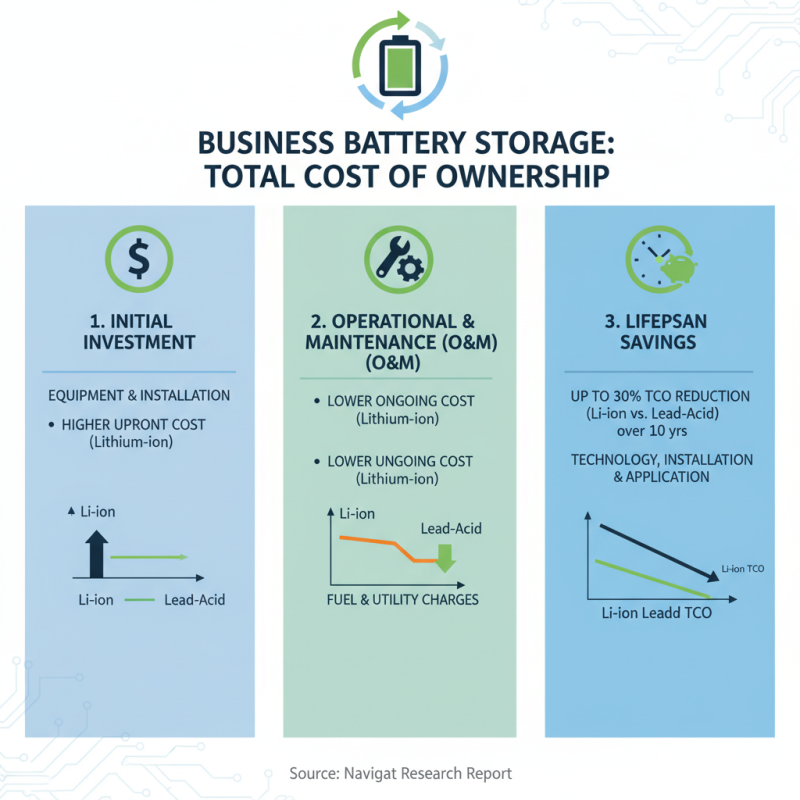
When considering battery storage systems for business, assessing the total cost of ownership (TCO) is crucial. TCO not only includes the initial investment but also considers operational and maintenance costs over the system's lifespan. A report by Navigant Research indicates that TCO can vary significantly based on technology used, installation complexity, and application type. For example, lithium-ion battery systems tend to have higher upfront costs but lower maintenance expenses. Some studies suggest TCO for these systems can drop by up to 30% over ten years compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
The life cycle of a battery also affects TCO. A state-of-the-art battery might last 10-15 years, depending on usage patterns. If a business anticipates rapid scaling, investing in higher-capacity systems may seem beneficial initially. However, managing energy demand becomes essential. Inefficient use of capacity can unexpectedly inflate operational costs. In addition, battery performance degradation over time often leads to diminished returns. Reports show that performance drops can average 15% over five years.
It’s essential to look beyond just the upfront costs. Consider potential energy savings, incentives, and rebates which can mitigate expenses. A thorough analysis may uncover gaps in expected vs. actual savings. Engaging with data from energy management studies can provide clearer insights into usage patterns and TCO. Ultimately, balancing cost with performance and scalability remains a continuous challenge. Reflecting on these factors helps businesses make informed decisions.
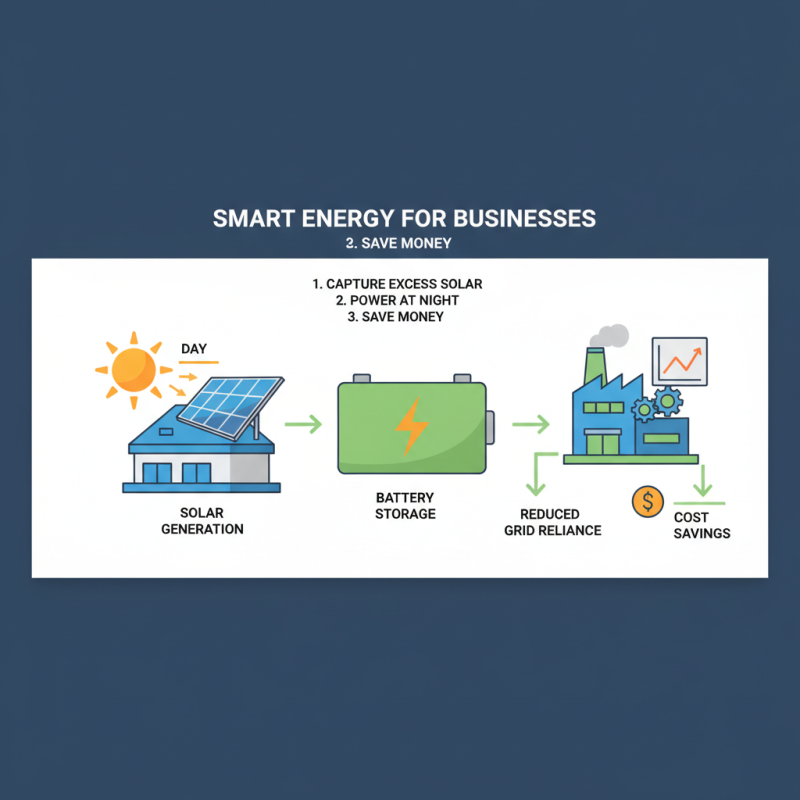
Integrating battery storage with renewable energy sources can significantly enhance efficiency for businesses. Imagine a solar installation on your rooftop, generating energy during the day. A commercial battery storage system can capture excess energy, allowing you to use it at night when your demand peaks. This not only reduces reliance on the grid but also cuts costs.
However, choosing the right battery storage can be challenging. Not every system suits every business. You need to consider your energy consumption patterns and peak hours. Some businesses may require more capacity than others. Thus, ongoing assessments are crucial.
Moreover, the technology in this field is rapidly changing. Newer, more efficient batteries frequently enter the market. Staying informed is essential but can also be overwhelming. You might feel hesitant when trying to keep pace with advancements. Engaging with energy consultants may clarify your options. Their insights can help you avoid costly mistakes while optimizing your setup.
When selecting the right commercial battery storage, understanding the factors influencing battery life and performance is crucial. Temperature is primary. Optimal performance occurs between 20°C to 25°C. Outside this range, battery efficiency drops significantly. A 2022 report indicated that a 10°C increase can decrease battery life by up to 30%.
Charging cycles also play a vital role. Frequent deep discharging and recharging can ultimately shorten battery lifespan. Data shows that lithium-ion batteries typically manage around 500 to 2,000 cycles, depending on usage. However, inconsistent charging patterns may reduce this significantly.
Moreover, the depth of discharge impacts performance. Exceeding 80% depth can cause irreversible damage over time. Many businesses overlook this aspect. Inconsistent discharging can lead to reduced energy capacity and unexpected failures.
Investing in a robust monitoring system can help track these factors. Just remember, data alone is not enough. It requires reflection on real-world applications and adjustments based on findings.
This bar chart illustrates the key factors influencing battery storage performance, showing the impact of capacity, charge cycles, temperature range, discharge rate, and depth of discharge on commercial battery systems.





