The rise of renewable energy has transformed the energy landscape. As energy demands grow, so does the need for efficient storage solutions. A Hybrid Energy Storage System (HESS) offers a flexible approach. According to a report by Research and Markets, the HESS market is expected to reach $13 billion by 2026, reflecting its increasing importance.
Expert Dr. Emily Hart, a leading voice in renewable technology, highlighted that "Hybrid Energy Storage Systems can optimize energy management effectively." This statement underscores the potential HESS holds as an innovative solution. By combining various technologies like batteries and supercapacitors, HESS provides advantages in both efficiency and cost.
Adopting a Hybrid Energy Storage System, however, poses challenges. Integration into existing grids can be complex. Also, varying operation conditions can impact performance. While these systems are promising, stakeholders must critically assess their implementation strategies. Balancing benefits and potential drawbacks is essential for successful adoption.

Hybrid Energy Storage Systems (HESS) combine multiple technologies to optimize energy storage. They typically integrate batteries and supercapacitors. This combination helps in addressing the limitations of each component. According to a recent market analysis, the global hybrid energy storage market is expected to grow significantly, reaching over $23 billion by 2026.
Batteries are great for long-duration storage. They hold energy for hours or days. On the other hand, supercapacitors excel in short bursts of energy. This is crucial for applications needing quick response times, like grid stabilization. A study from the International Renewable Energy Agency indicates that systems combining these technologies can enhance performance by up to 50%.
Hybrid systems also face challenges. Their complexity can lead to maintenance issues. Moreover, the initial setup cost might deter smaller projects. Yet, the efficiency gains often justify these expenses. Investing in such technology can be beneficial, but careful planning is essential. A balanced approach is needed to maximize both performance and reliability.
Hybrid energy storage systems combine different technologies to offer enhanced performance. These systems often integrate batteries with ultra-capacitors or flywheels. This combination allows them to store energy more efficiently and release it quickly when needed. Such flexibility is essential in managing fluctuating energy demands.
One significant advantage of hybrid systems is their longevity. Many conventional systems experience rapid degradation. In contrast, hybrid systems benefit from the strengths of each component, resulting in a longer lifespan. This longevity often translates to lower replacement costs and less environmental waste. Hybrid systems also provide improved energy density, enabling efficient energy storage in a smaller footprint.
Cost-effectiveness is another key area where hybrid systems shine. While initial costs may be higher, the overall operational efficiency reduces long-term expenses. However, this transition may require some upfront analysis and investment. Proper integration and monitoring are crucial for maximizing benefits. Simply adopting hybrid technology without strategic planning can lead to subpar results.
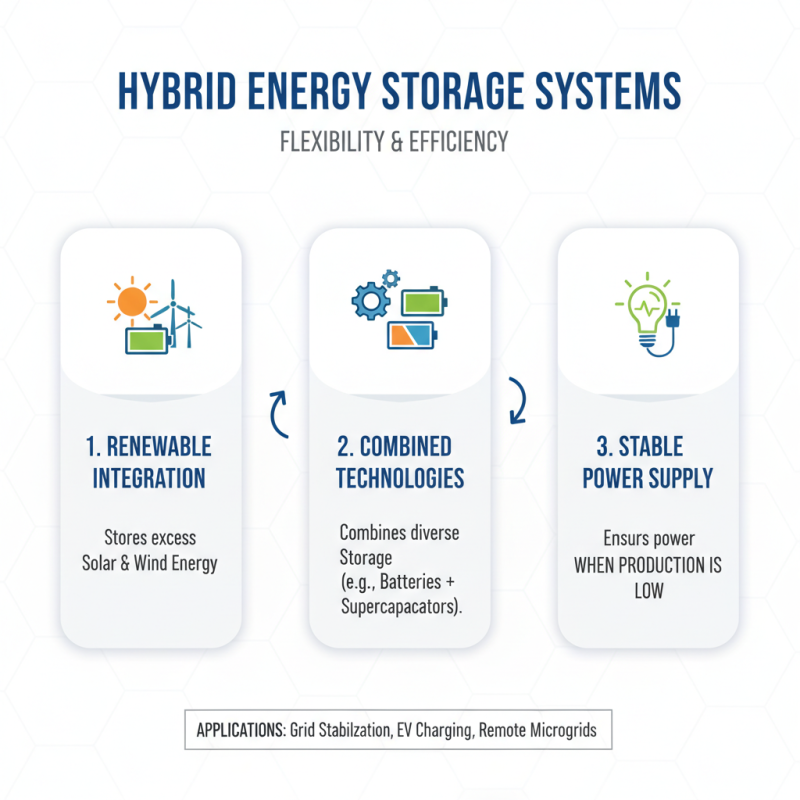
In various industries, hybrid energy storage systems are gaining traction. These systems combine different storage technologies, offering flexibility and efficiency. For instance, in renewable energy projects, they store excess solar and wind energy. This energy can be used when production is low, ensuring a stable supply.
The transportation sector also benefits from hybrid systems. Electric vehicles utilize these technologies to extend range and reduce charging times. By integrating batteries with supercapacitors, vehicles can deliver quick bursts of power. However, this approach may not be suitable for all models, leading to mixed results on performance.
Industrial applications are showing promise too. Factories use hybrid systems to manage peak loads. This helps prevent outages and reduces energy costs. Yet, some industries struggle with integration challenges, indicating a need for better solutions. Each application presents unique aspects and hurdles, calling for careful consideration.
When considering a hybrid energy storage system, it's crucial to evaluate your specific needs. Different applications demand unique solutions. For instance, some systems are better suited for renewable energy integration. Others might excel in grid stability. Understanding these requirements can lead to efficient energy management.
Cost is a vital factor. Hybrid systems may come with higher upfront costs. Yet, they often provide long-term savings. Performance is another consideration. How long can the system store energy? Will it meet peak demand effectively? These aspects are essential for maximizing efficiency.
Space availability can inhibit certain choices. A compact design might be necessary for urban settings. Additionally, pay attention to the system's lifecycle. How long can you realistically use it? Maintenance is often overlooked. It’s important to assess long-term reliability. Making the right choice requires reflection. Not all needs are straightforward; sometimes, compromises may be necessary.
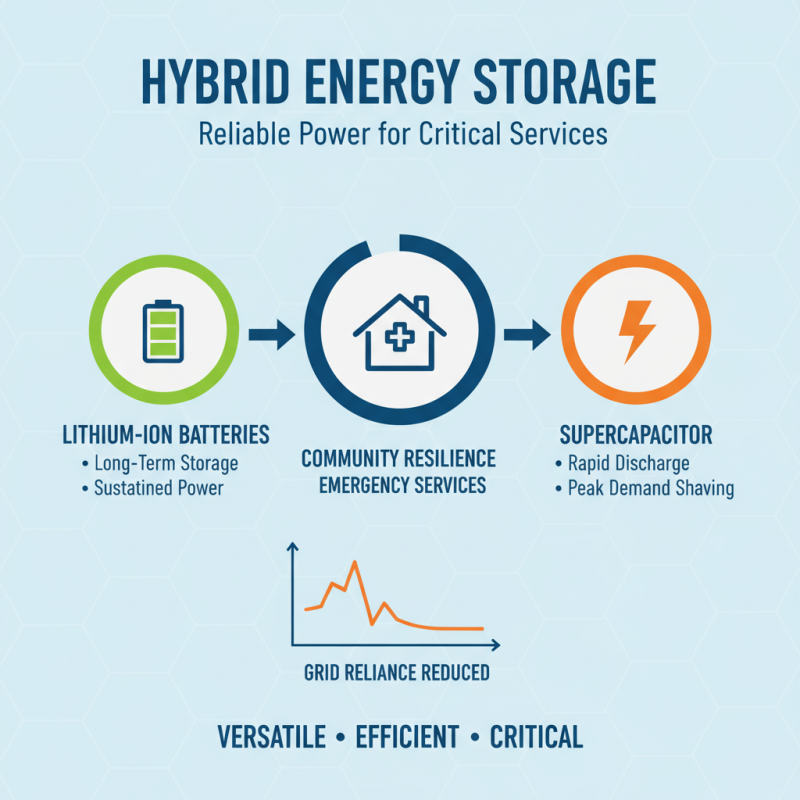
Hybrid energy storage systems have gained traction in various sectors, thanks to their versatility. One notable case involved a community in need of reliable power for emergency services. They combined lithium-ion batteries with a supercapacitor. This combination offered rapid energy discharge while ensuring long-term energy storage. It proved effective during peak demand hours, reducing reliance on traditional grids.
Another case study from a commercial facility revealed mixed results. The aim was to maximize energy efficiency with a hybrid system. They used lead-acid batteries alongside newer technologies. While initial results showcased improved energy savings, maintenance challenges arose. The aging lead-acid batteries created unforeseen costs. This scenario highlights the need for ongoing evaluation and adaptation.
In both examples, real-world implementations brought both successes and challenges. Organizations must carefully assess their needs to choose the best configuration. Each hybrid solution requires ongoing monitoring to ensure optimal performance. The journey toward effective energy storage is often filled with learning opportunities.





