As the demand for sustainable energy solutions continues to rise, the significance of Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) has become increasingly apparent. BESS plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency, enabling the integration of renewable energy sources, and providing reliable power during peak consumption periods. This technology allows for the storage of excess energy generated from renewable sources, such as solar and wind, to be utilized when demand is high or production falls short, thereby creating a more resilient energy grid.
In recent years, advancements in battery technology have further propelled the development of BESS, making it a viable option not only for utility-scale applications but also for residential and commercial use. These systems offer a multitude of benefits, including reduced energy costs, improved grid stability, and lower reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, the growing focus on energy independence and security drives interest in BESS, as it empowers users to manage their energy consumption effectively.
Looking ahead, the future trends in Battery Energy Storage Systems indicate a promising trajectory. Innovations in battery materials, efficiency, and lifecycle management are expected to enhance the performance of BESS even further. As policies and regulations evolve to support the transition to sustainable energy, BESS is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping an eco-friendly energy landscape, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.

Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS)
play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and reliability of power systems. At their core, BESS are designed to store electrical energy for later use, thus enabling a more flexible response to fluctuations in energy demand and supply. These systems can be deployed in a variety of applications, including renewable energy integration, grid stabilization, and peak shaving. By absorbing excess energy during low-demand periods and releasing it during peak times, BESS help balance load and support overall grid functionality.
The technology behind BESS has evolved significantly over recent years, leading to improvements in energy density, lifespan, and cost-effectiveness. Various battery chemistries, such as lithium-ion, flow batteries, and solid-state batteries, offer differing advantages for specific applications. As the global demand for clean energy continues to grow, the development of more efficient and sustainable battery storage solutions is critical. Innovations in this sector are paving the way for future trends, such as the integration of artificial intelligence for real-time data analytics and performance optimization, and the potential for decentralized energy systems that empower consumers to manage their own energy storage.
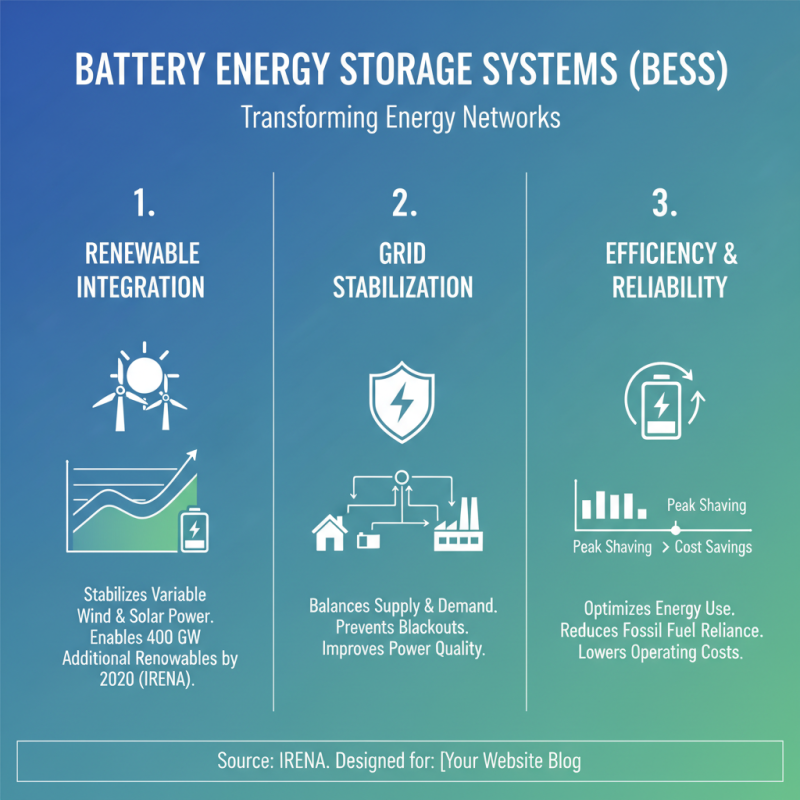
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) have emerged as a pivotal technology in transforming energy networks, offering a range of key benefits that enhance the efficiency and reliability of electricity supply. One of the primary advantages of BESS is the ability to facilitate renewable energy integration. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), energy storage could enable up to 400 GW of additional renewable energy capacity by 2030, effectively mitigating the variability of sources such as wind and solar. This capability not only stabilizes the grid but also optimizes the use of generated renewable energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Furthermore, BESS enhances energy management by allowing for peak shaving and load leveling. A report by the U.S. Department of Energy estimates that energy storage can significantly reduce peak demand charges, which make up about 30% of a commercial customer's electricity bill. By discharging stored energy during peak periods, businesses and utilities can lower operational costs and improve overall system resilience. Additionally, BESS contributes to frequency regulation and ancillary services, ensuring a stable and reliable electricity supply that can adapt to fluctuating demand.
As energy systems evolve, the role of BESS will become increasingly crucial. With the global energy storage market projected to reach approximately $546.2 billion by 2035, the adoption of these systems in energy networks not only addresses the immediate challenges of energy transition but also positions utilities and consumers for a sustainable and economically viable energy future.
Technological innovations are rapidly shaping the landscape of Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), enhancing their efficiency, capacity, and integration in various applications. One significant advancement is the development of advanced battery chemistries, such as lithium-sulfur and solid-state batteries, which promise increased energy density and longer life cycles. These technologies not only provide a higher performance but also contribute to safer storage solutions, reducing the risks associated with traditional lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, improvements in battery management systems (BMS) allow for better monitoring and control, further optimizing energy usage and extending battery life.
Tips: When considering BESS for your applications, pay attention to the specific energy needs and potential operational environments. Different battery technologies offer various advantages depending on the use case—for instance, solid-state batteries may excel in high-temperature environments where safety is a concern.
Another trend is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning into BESS management. By analyzing usage patterns and predicting energy demands, AI can optimize the charging and discharging processes, ensuring that energy storage is as efficient as possible. This not only helps in maximizing the performance of BESS but also in reducing overall operational costs. Emphasizing these technological advancements can enhance energy resilience and support the transition to renewable energy sources.
Tips: Stay informed about the latest developments in battery technology by following industry publications and engaging with community forums. This will help you make informed decisions when selecting energy storage solutions suitable for your specific needs.
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) represent a significant advancement in energy management, yet several challenges impede their widespread adoption. One of the primary barriers is the high initial investment required for installation and integration. According to a report from the International Energy Agency (IEA), the capital costs for lithium-ion battery systems can range between $300 to $700 per kWh, which could be prohibitive for many companies considering the switch. Moreover, fluctuations in raw material prices, influenced by market volatility, lead to uncertainty in future investment returns, discouraging potential adopters.
Another significant challenge lies in regulatory and policy frameworks. Many regions lack clear guidelines or incentives for BESS deployment, resulting in a complex landscape that can deter investment. The U.S. Energy Storage Association emphasizes the importance of streamlined interconnection processes and supportive policies to foster growth in this sector. While some local governments have begun to implement programs to incentivize energy storage, a cohesive national strategy is still missing, which could unify various efforts and stimulate adoption.
Tip: When considering BESS for your organization, conducting a comprehensive feasibility study can help you evaluate potential costs and savings, ensuring informed decision-making. Additionally, staying abreast of evolving regulations is crucial, as supportive policy changes can significantly enhance the viability of battery storage projects.
As the demand for renewable energy sources continues to surge, Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are emerging as a crucial component in achieving a sustainable energy future. Market trends indicate a growing inclination towards integrating BESS in both residential and commercial sectors. This shift is primarily driven by the need for grid stability and the increasing penetration of intermittent energy sources like wind and solar. Policymakers are recognizing the importance of these systems, leading to supportive regulations and incentive programs that foster their adoption. This includes tax credits, rebates, and funding for research and development aimed at enhancing battery technologies.
Furthermore, the global energy landscape is witnessing a shift in policy frameworks that prioritize clean energy transition. Governments are increasingly setting ambitious renewable energy targets and climate goals that compel the integration of BESS into energy infrastructures. This not only provides a pathway for distributed energy resources but also enhances resilience against power outages and extreme weather events. As utilities and private sectors collaborate, the momentum for BESS development is expected to gain traction, resulting in lower costs and improved technology. The future trends in BESS look promising, with innovations leading to more efficient, longer-lasting, and environmentally friendly solutions that align with global energy aspirations.
| Dimension | Data Point | 2023 Estimate | Growth Rate (2023-2030) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Market Size (USD Billion) | Battery Energy Storage Systems | 15.6 | 20% |
| Average System Cost (USD/kWh) | Lithium-ion BESS | 300 | -5% |
| Capacity Additions (GWh) | Annual Global Additions | 18 | 30% |
| Government Support (USD Billion) | Incentives for BESS | 4.5 | Varies |
| Percentage of Renewable Integration (%) | BESS role in renewables | 35 | - |





